Where is germanium generally used? How much does germanium recycling cost per gram today?
Germanium, as a strategic resource occupying a pivotal role in modern
technology, shines with an indispensable light in many high-end
technological fields due to its unique and excellent physical and
chemical properties.
In the highly sophisticated and competitive semiconductor industry,
germanium is like a magical "wizard". As a key doping element, it can
skillfully optimize the performance of transistors. When it is
integrated, it is like injecting a mysterious force into the transistor,
making the movement of electrons in the semiconductor material more
orderly and efficient. This optimization of transistor performance is
not just a simple improvement, but a qualitative leap for the entire
semiconductor device and even a wider range of electronic equipment. For
example, in the chip manufacturing of high-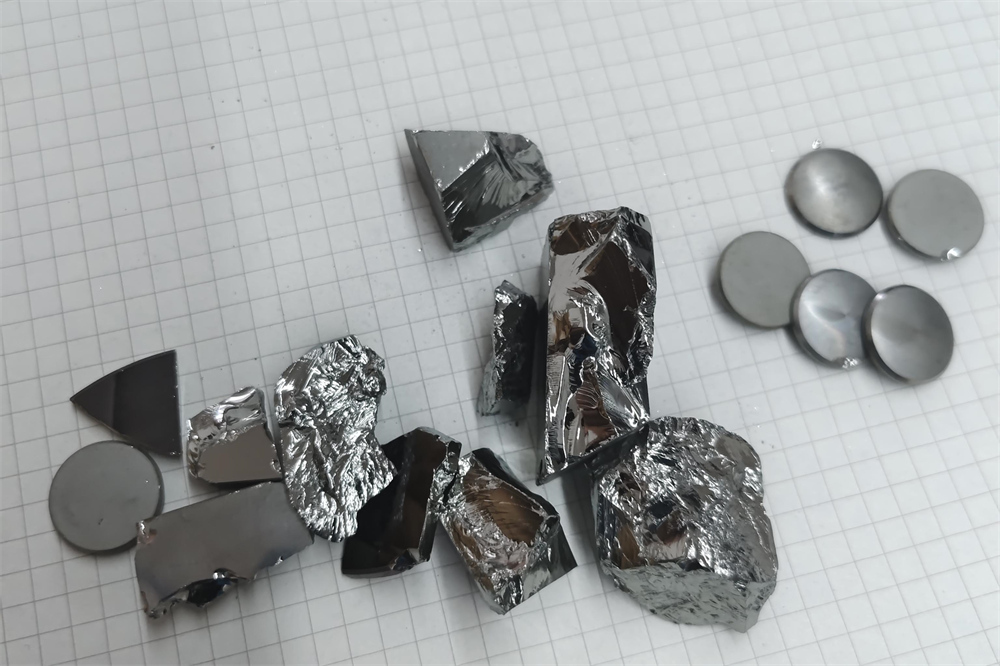 performance computers, the
doping of germanium can enable the chips to have faster processing
speeds and lower power consumption, which is like injecting powerful
power into the "brain" of computers, enabling them to handle complex
tasks with ease, and thus promoting the rapid development of the entire
information technology industry.
In the field of optical fiber communication, which is like a "highway"
for information transmission, germanium plays a crucial role as a
"guardian" ensuring the high-speed transmission of information. Optical
fiber communication is a vast and complex network, with each optical
fiber being a "vein" of information transmission, and germanium is one
of the key factors that keep these "vessels" clear. It can make optical
signals transmit stably in the optical fiber, reducing signal
attenuation and distortion, just like providing a clear, wide and
interference-free "channel" for the spread of information. Whether it is
long-distance international communication or high-speed network
connections within cities, germanium plays a vital role, enabling people
to conduct efficient information exchange anytime and anywhere, which
has greatly changed people's lives and working styles.
In the mysterious field of infrared optics, germanium stands out. It is
like a skilled craftsman used to manufacture high-precision infrared
devices. In the military field, infrared night vision goggles use key
components made of germanium to enable soldiers to see the surrounding
performance computers, the
doping of germanium can enable the chips to have faster processing
speeds and lower power consumption, which is like injecting powerful
power into the "brain" of computers, enabling them to handle complex
tasks with ease, and thus promoting the rapid development of the entire
information technology industry.
In the field of optical fiber communication, which is like a "highway"
for information transmission, germanium plays a crucial role as a
"guardian" ensuring the high-speed transmission of information. Optical
fiber communication is a vast and complex network, with each optical
fiber being a "vein" of information transmission, and germanium is one
of the key factors that keep these "vessels" clear. It can make optical
signals transmit stably in the optical fiber, reducing signal
attenuation and distortion, just like providing a clear, wide and
interference-free "channel" for the spread of information. Whether it is
long-distance international communication or high-speed network
connections within cities, germanium plays a vital role, enabling people
to conduct efficient information exchange anytime and anywhere, which
has greatly changed people's lives and working styles.
In the mysterious field of infrared optics, germanium stands out. It is
like a skilled craftsman used to manufacture high-precision infrared
devices. In the military field, infrared night vision goggles use key
components made of germanium to enable soldiers to see the surrounding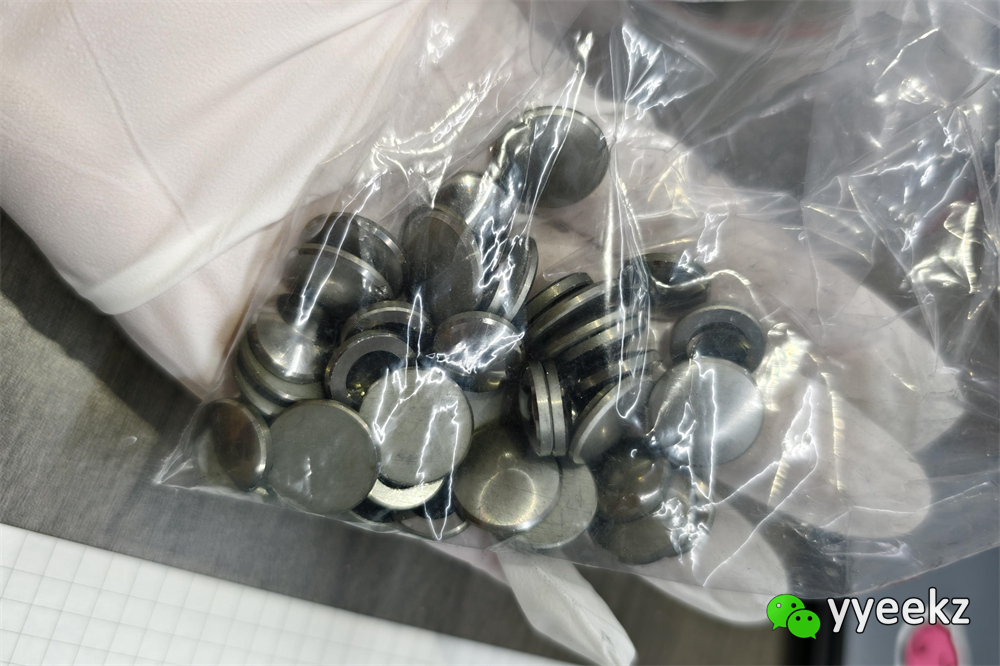 environment clearly at night, just like wearing a pair of "night vision
goggles", which greatly improves the concealment and safety of combat.
In the civilian aspect, infrared thermal imagers utilize the
characteristics of germanium to detect infrared radiation emitted by
objects, so as to discover hidden objects or monitor the operating
status of equipment in dark or smoky environments, and are widely used
in security monitoring, industrial inspection and other fields.
In view of the extensive application of germanium in such numerous
fields and its significant role in promoting scientific and
technological progress, the market demand for high-purity germanium is
like an ever-flowing "fountain" and has always been high. This strong
demand not only stems from the reliance of traditional technological
fields on germanium, but also becomes more intense with the continuous
emergence of new technologies. For example, in cutting-edge fields such
as quantum computing and artificial intelligence, germanium also has
potential huge application value, which has led researchers and
enterprises around the world to compete for high-purity germanium
resources.
This also makes the recycling of germanium a highly economical activity.
In today's era of increasingly scarce resources, the recycling of
germanium is like digging treasures from "ruins". Every discarded device
containing germanium may be a "pearl" hiding great value. According to
today's market analysis, the recycling price of one gram of high-purity
germanium is about 10 yuan. However, behind this seemingly low price
lies profound market logic.
environment clearly at night, just like wearing a pair of "night vision
goggles", which greatly improves the concealment and safety of combat.
In the civilian aspect, infrared thermal imagers utilize the
characteristics of germanium to detect infrared radiation emitted by
objects, so as to discover hidden objects or monitor the operating
status of equipment in dark or smoky environments, and are widely used
in security monitoring, industrial inspection and other fields.
In view of the extensive application of germanium in such numerous
fields and its significant role in promoting scientific and
technological progress, the market demand for high-purity germanium is
like an ever-flowing "fountain" and has always been high. This strong
demand not only stems from the reliance of traditional technological
fields on germanium, but also becomes more intense with the continuous
emergence of new technologies. For example, in cutting-edge fields such
as quantum computing and artificial intelligence, germanium also has
potential huge application value, which has led researchers and
enterprises around the world to compete for high-purity germanium
resources.
This also makes the recycling of germanium a highly economical activity.
In today's era of increasingly scarce resources, the recycling of
germanium is like digging treasures from "ruins". Every discarded device
containing germanium may be a "pearl" hiding great value. According to
today's market analysis, the recycling price of one gram of high-purity
germanium is about 10 yuan. However, behind this seemingly low price
lies profound market logic.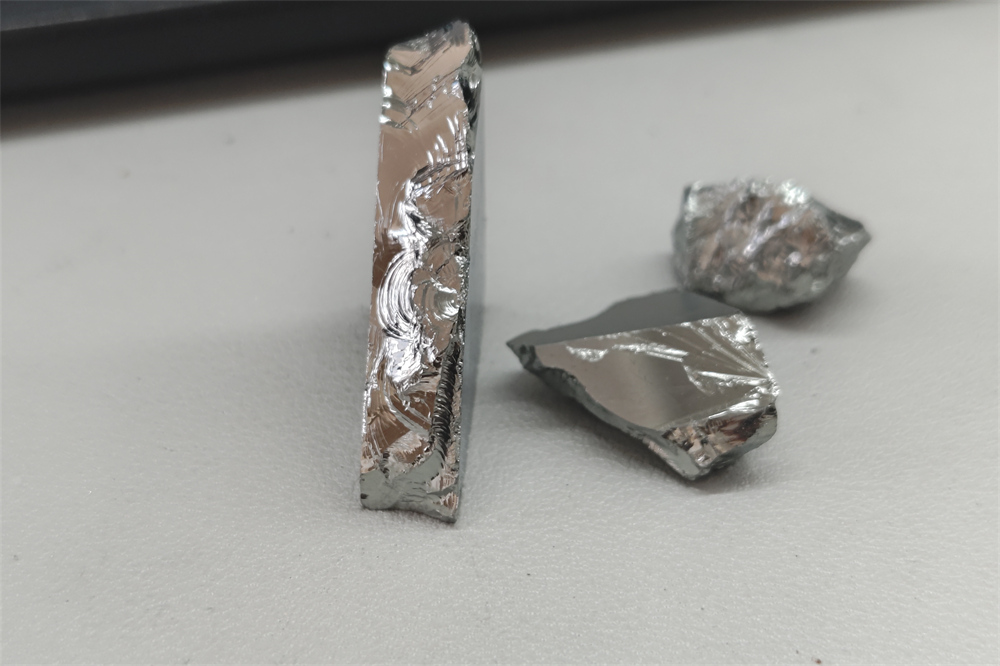 Considering the key role of germanium in
those high-value application fields, such pricing actually reflects the
full recognition of the market for its scarcity and importance. After
all, the mining and purification of germanium are not easy tasks,
requiring complex technology and high costs, while recycling is a more
efficient and sustainable way of obtaining it.
Furthermore, the calculation shows that one kilogram of high-purity
germanium can reach a value of tens of thousands of yuan according to
the current market price. This remarkable figure not only reflects the
high value of germanium as a strategic resource, but also profoundly
reveals that in specific high-tech industries, even a trace amount of
material can generate huge economic benefits. In those high-end
technological fields, often only a very small amount of germanium is
needed to significantly improve product performance, thereby bringing
high profit returns. Therefore, whether from the perspective of resource
reuse to achieve sustainable development and reduce the dependence on
native germanium mines, or from the perspective of economic benefits,
the recycling of germanium is a field worthy of great attention and
investment. It is like a bridge connecting the past and the future,
technology and environmental protection, economy and development,
opening a door to a better technological world for us.
Considering the key role of germanium in
those high-value application fields, such pricing actually reflects the
full recognition of the market for its scarcity and importance. After
all, the mining and purification of germanium are not easy tasks,
requiring complex technology and high costs, while recycling is a more
efficient and sustainable way of obtaining it.
Furthermore, the calculation shows that one kilogram of high-purity
germanium can reach a value of tens of thousands of yuan according to
the current market price. This remarkable figure not only reflects the
high value of germanium as a strategic resource, but also profoundly
reveals that in specific high-tech industries, even a trace amount of
material can generate huge economic benefits. In those high-end
technological fields, often only a very small amount of germanium is
needed to significantly improve product performance, thereby bringing
high profit returns. Therefore, whether from the perspective of resource
reuse to achieve sustainable development and reduce the dependence on
native germanium mines, or from the perspective of economic benefits,
the recycling of germanium is a field worthy of great attention and
investment. It is like a bridge connecting the past and the future,
technology and environmental protection, economy and development,
opening a door to a better technological world for us.